Two gliders are on a frictionless level air track, setting the stage for an exploration of motion and interactions. This captivating scenario provides a unique opportunity to delve into the fundamental principles governing the behavior of objects in motion, revealing the intricate interplay between energy, momentum, and conservation laws.
The absence of friction on the air track eliminates a significant force that typically impedes motion, allowing us to isolate and study the inherent characteristics of the gliders. As they glide effortlessly along the track, their interactions, whether collisions or elastic rebounds, offer insights into the fundamental principles of mechanics.
Two Gliders on a Frictionless Level Air Track

The motion of two gliders on a frictionless level air track provides a simplified system to study fundamental concepts in mechanics, including conservation laws, energy transformations, and momentum.
Concept of Two Gliders on a Frictionless Level Air Track, Two gliders are on a frictionless level air track
A frictionless level air track is a laboratory apparatus that allows objects to glide with minimal resistance. When two gliders are placed on such a track, they can move freely in one dimension without any external forces acting upon them.
Motion and Interactions
In the absence of friction, the gliders move with constant velocity or accelerate at a constant rate if an external force is applied. The gliders can interact with each other through collisions or elastic rebounds, conserving momentum and energy.
Conservation Laws
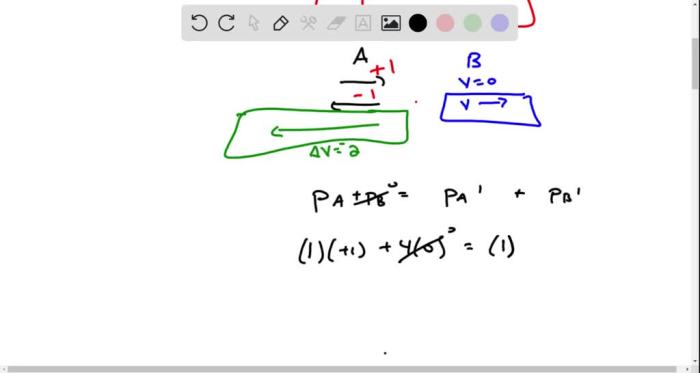
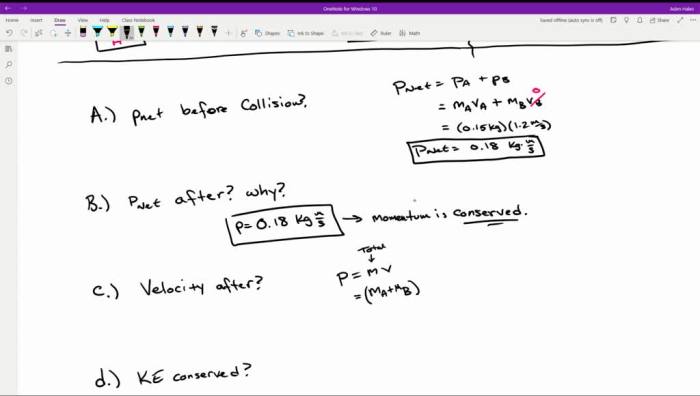
- Conservation of Momentum:The total momentum of the system of two gliders remains constant during any interaction, including collisions and rebounds.
- Conservation of Energy:The total energy of the system, including kinetic and potential energy, remains constant if no external forces are acting upon it.
Energy Transformations
As the gliders move, kinetic energy is converted into potential energy and vice versa. This energy transformation is elastic in the case of rebounds and inelastic in the case of collisions.
Momentum and Impulse
During collisions, the momentum of the gliders changes instantaneously. The change in momentum is equal to the impulse, which is the product of the force and the time interval over which it acts.
Experimental Considerations
Experimental setups involving two gliders on an air track can be used to verify the conservation laws and study the dynamics of the system. Measurements of position, velocity, and force can be obtained using sensors and data acquisition systems.
Applications and Real-World Examples
The concepts learned in this analysis have applications in various fields, including:
- Transportation:Understanding the motion of vehicles on frictionless surfaces, such as air hockey tables and ice rinks.
- Collision Analysis:Investigating the dynamics of collisions in automotive accidents and sports.
- Energy Conservation:Designing systems that maximize energy efficiency and minimize losses.
Questions and Answers: Two Gliders Are On A Frictionless Level Air Track
What is a frictionless level air track?
A frictionless level air track is a specialized apparatus used in physics experiments to minimize friction, allowing objects to move freely with minimal resistance.
How does the absence of friction affect the motion of the gliders?
In the absence of friction, the gliders move with constant velocity, maintaining their initial momentum unless acted upon by an external force.
What is the significance of conservation laws in this system?
Conservation laws, such as the conservation of energy and momentum, govern the interactions between the gliders, ensuring that total energy and momentum remain constant throughout the system.