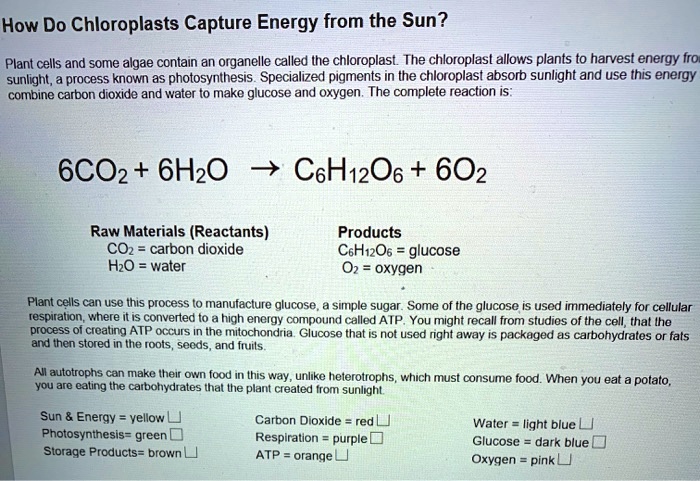
How do chloroplasts capture energy from the sun worksheet answers – Embark on a journey to unravel the intricate mechanisms of photosynthesis, a process that sustains life on Earth. This exploration delves into the fascinating world of chloroplasts, the organelles responsible for capturing sunlight and converting it into usable energy.
Chloroplasts, the powerhouses of plant cells, orchestrate a remarkable symphony of light absorption, energy transfer, and biochemical reactions to produce the very foundation of life—glucose. This comprehensive guide unravels the intricacies of photosynthesis, shedding light on the remarkable process by which chloroplasts capture energy from the sun.
Photosynthesis and the Role of Chloroplasts: How Do Chloroplasts Capture Energy From The Sun Worksheet Answers
Photosynthesis is a vital process in which plants and other organisms convert light energy into chemical energy, which is stored in glucose. This process not only provides sustenance for plants but also releases oxygen into the atmosphere, making it crucial for life on Earth.
Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells that play a central role in photosynthesis. They contain chlorophyll, a green pigment that absorbs sunlight and initiates the process of converting light energy into chemical energy.
Light Absorption and Energy Transfer
Chlorophyll and other pigments in chloroplasts absorb sunlight. The energy from the absorbed light is then transferred through a series of electron carriers within the chloroplast. This energy transfer is essential for driving the chemical reactions that convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose.
Accessory pigments, such as carotenoids and phycobilins, broaden the absorption spectrum of chloroplasts, allowing them to absorb a wider range of wavelengths of light.
The Light-Dependent Reactions, How do chloroplasts capture energy from the sun worksheet answers
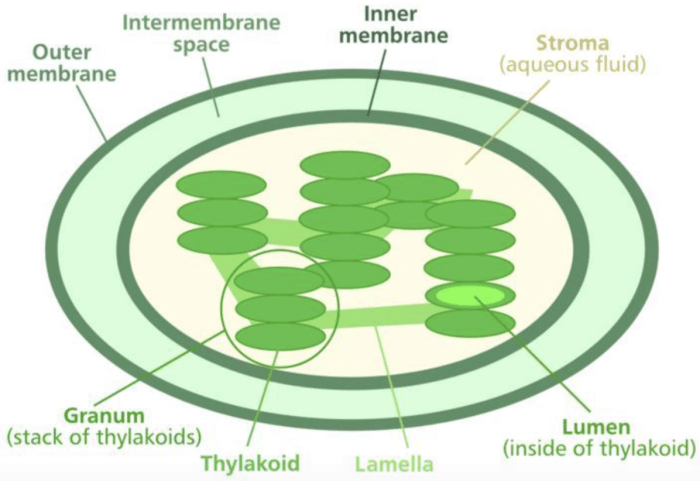
The light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis occur in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts. These reactions involve the splitting of water molecules, the generation of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), and the reduction of NADP+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate). The energy from sunlight is used to drive these reactions.
Photosystem I and photosystem II are two protein complexes involved in the light-dependent reactions. Photosystem II absorbs light energy and uses it to split water molecules, releasing oxygen as a byproduct. Photosystem I absorbs light energy and uses it to reduce NADP+.
| Photosystem I | Photosystem II |
|---|---|
| Absorbs light at 700 nm | Absorbs light at 680 nm |
| Uses light energy to reduce NADP+ | Uses light energy to split water |
| Releases oxygen as a byproduct | Does not release oxygen |
The Calvin Cycle
The Calvin cycle, also known as the light-independent reactions, occurs in the stroma of chloroplasts. In this cycle, carbon dioxide is fixed and converted into glucose using the energy from ATP and NADPH generated in the light-dependent reactions.
The Calvin cycle is a cyclic process that involves three main steps: carbon fixation, reduction, and regeneration. The enzyme ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (Rubisco) catalyzes the initial step of carbon fixation.
Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
Several factors can influence the rate of photosynthesis, including light intensity, temperature, and carbon dioxide concentration.
- Light intensity:The rate of photosynthesis increases with increasing light intensity until a plateau is reached.
- Temperature:The rate of photosynthesis increases with increasing temperature up to an optimum temperature, beyond which it decreases.
- Carbon dioxide concentration:The rate of photosynthesis increases with increasing carbon dioxide concentration.
FAQ Insights
What is the primary function of chloroplasts?
Chloroplasts are the organelles responsible for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy.
How do chloroplasts capture light energy?
Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll and other pigments that absorb specific wavelengths of light, converting the energy into electrical energy.
What are the two main stages of photosynthesis?
The two main stages of photosynthesis are the light-dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle (light-independent reactions).
What is the significance of accessory pigments in photosynthesis?
Accessory pigments broaden the absorption spectrum of chloroplasts, allowing them to capture a wider range of wavelengths of light.